In a world where data breaches make headlines weekly, the old security model of "trust but verify" no longer cuts it. Zero Trust flips this approach on its head with a simple but powerful principle: "never trust, always verify." This mindset shift is revolutionizing how we protect our most valuable digital assets—especially APIs, which have become prime targets for attackers.
The Colonial Pipeline breach showed us what happens when security fails: a single compromised password led to massive disruption. For APIs specifically, the stakes are even higher since they often provide direct pathways to sensitive data and critical functionality.
Let's dive into why Zero Trust matters for API security and how you can implement it effectively in your organization.
- Demolishing the Castle Walls: Why Traditional Security Falls Short
- Trust Nothing: The Non-Negotiable Principles of API Security
- Architect for Suspicion: Crafting Your Zero Trust Framework
- Exposing the Invisible: Hunting Down Rogue APIs
- Fortify the Gates: Advanced Infrastructure That Actually Works
- Breaking Through Barriers: Conquering Zero Trust Challenges
- Security Without Friction: Keeping Developers Happy
- The Security Crystal Ball: What's Next for Zero Trust
- From Vulnerable to Vigilant: Take Action Today
Demolishing the Castle Walls: Why Traditional Security Falls Short
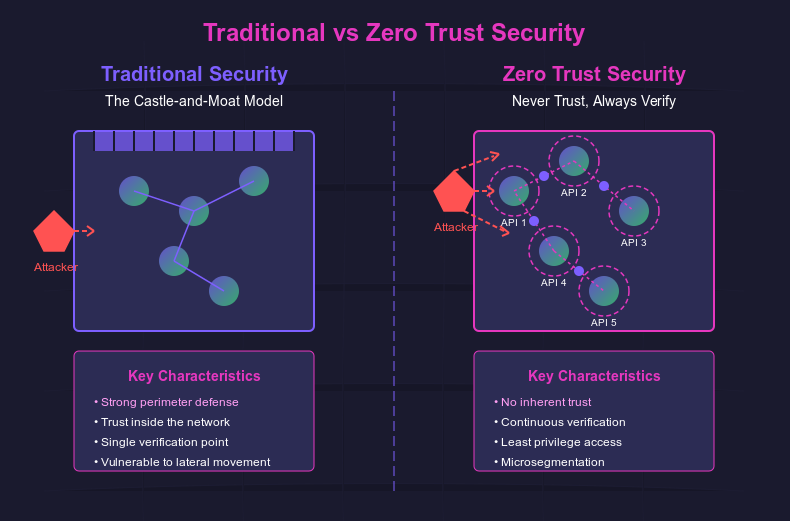
Traditional security was built like medieval castles—hard outer walls with relatively free movement inside. Zero Trust takes a completely different approach, treating every request as potentially hostile.
The Fundamental Shift
Zero Trust security completely abandons the outdated "castle-and-moat" model where only outsiders were considered threats. Instead, it acknowledges a harsh reality: threats can come from anywhere, including inside your network. This approach eliminates the concept of implicit trust regardless of where users or devices are located.
Five Key Principles
At its core, Zero Trust operates on five critical principles:
- Know your protect surface (what you're actually securing)
- Understand existing security controls
- Incorporate modern architecture and tools
- Apply detailed policy
- Continuously monitor and alert
Why Traditional Security Falls Short
When VPN credentials get compromised—as dramatically demonstrated by the Colonial Pipeline breach—the entire traditional security model collapses. Once attackers breach the perimeter, they often move laterally throughout the network with minimal resistance.
In API environments, this can be particularly devastating as APIs serve as direct conduits to sensitive data and critical functionality. The fundamental weakness? Relying on implicit trust after a single authentication point.
Trust Nothing: The Non-Negotiable Principles of API Security
Zero Trust isn't just a buzzword—it's a comprehensive security approach with specific principles that directly apply to API protection. Understanding these principles helps build truly secure API ecosystems.
No Inherent Trust
The first essential principle eliminates implicit trust entirely. Under Zero Trust, no user, device, or system is trusted by default—whether they're inside or outside your network.
For APIs, this means:
- Each API call is verified independently regardless of source
- Authentication happens continuously, not just at login
- Access is granted based on identity and role, not location
Continuous Verification
Rather than authenticating users once at the perimeter, Zero Trust demands ongoing verification throughout the user's session. The system constantly evaluates:
- Identity and role
- Device security posture
- Time of day
- Geolocation
- Data sensitivity
Even previously authorized users may be denied connections if suspicious contextual factors emerge, creating a dynamic security environment that adapts to changing conditions.
Least Privilege Access
This principle ensures users only access specific resources they need to perform their job functions—nothing more. Once authenticated, users only see the applications they're authorized to use, while all other network resources remain hidden.
For APIs, implementing least privilege means:
- Defining granular permissions for each endpoint
- Limiting data exposure to only what's necessary
- Restricting administrative functionality to appropriate roles using Role-Based Access Control
Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation divides your network into secure zones, containing potential threats and preventing lateral movement. When applied to APIs, it allows you to implement granular, role-based access policies that secure individual endpoints.
Each API becomes its own micro-perimeter with distinct access controls. The benefit? Even if one API is compromised, the damage is contained and doesn't spread to other systems or data.
Architect for Suspicion: Crafting Your Zero Trust Framework
Implementing Zero Trust requires a structured approach and a robust API management solution. Here's a practical framework to secure your APIs using Zero Trust principles.
Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms
Strong authentication and authorization form the cornerstone of any Zero Trust implementation. For APIs, consider these key methods. Implementing effective authentication and rate-limiting strategies enhances API security.
JWT Validation
JSON Web Tokens provide a compact, self-contained way to securely transmit information between parties. A proper JWT implementation for APIs should:
- Verify token signatures using strong algorithms
- Validate all claims, including expiration time
- Check permissions before allowing access
- Implement token revocation capabilities
OAuth 2.0 Flows
For applications requiring more complex authorization, OAuth 2.0 provides a robust framework. When implementing OAuth for APIs:
- Use authorization code flow with PKCE for secure token exchange
- Implement short-lived access tokens with refresh tokens
- Validate scopes against requested resources
- Consider using a proven identity provider rather than building your own
API Keys with Rate Limiting
For simpler services, API keys combined with proper rate limiting can provide adequate security. Effective methods for managing API access include:
- Store API keys securely (never in code repositories)
- Implement granular permissions for each key
- Implement rate limiting to prevent abuse
- Rotate keys regularly and have a clean revocation process
Continuous Validation Techniques
Zero Trust moves beyond point-in-time authentication to continuous validation throughout each session. Monitoring API usage is essential to this process.
Session Monitoring
Implement active monitoring during API sessions using effective API monitoring tools:
- Check for anomalies in request patterns
- Monitor for changes in device fingerprints
- Track unusual API call sequences
- Implement automatic session termination for suspicious activity
Contextual Access Decisions
Make authorization decisions based on multiple factors beyond just credentials:
- User identity and role
- Device security posture
- Location and network information
- Time of day and historical usage patterns
- Risk score based on multiple factors
Exposing the Invisible: Hunting Down Rogue APIs
The adage "you can't protect what you can't see" perfectly captures the challenge of API security. As organizations rapidly deploy APIs, maintaining visibility becomes increasingly difficult.
The Shadow API Problem
Shadow or rogue APIs—those existing outside formal management processes—represent significant security risks. They often lack proper security controls and may expose sensitive data without appropriate protections.
Discovery Techniques
To effectively identify rogue APIs within your organization:
- Source Code Introspection: Systematically examine your code repositories to uncover hidden API artifacts. This helps identify APIs developed without proper documentation or security oversight.
- Network Traffic Inspection: Deploy tools that monitor network traffic in real-time to detect API calls and endpoints missing from your official inventory. This runtime discovery reveals shadow APIs actively being used in your environment.
- API Gateway Monitoring: Configure API gateways to log and report on all traffic, helping identify unauthorized or undocumented endpoints that bypass your security controls.
Building an Accurate API Inventory
An up-to-date inventory forms the foundation of effective API security governance:
- Standardized Documentation: Establish clear processes for how new APIs are introduced and tracked within your organization. Require security review before deployment.
- Centralized Tracking: Implement a centralized platform for managing your API inventory rather than relying on spreadsheets or manual methods that quickly become outdated.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic reviews to identify shadow and zombie APIs that require either proper integration into your security program or deprecation to reduce your attack surface.
Fortify the Gates: Advanced Infrastructure That Actually Works
Implementing advanced infrastructure components creates robust protection layers for your APIs while improving both security and performance. A strong API infrastructure is essential to achieving this balance.
API Gateways as Security Enforcers
API gateways serve as the primary entry point for all API calls, acting as the first line of defense against potential threats:
- Access Control Enforcement: Gateways validate tokens, authenticate users, and enforce permissions before requests reach your backend services, centralizing security policy enforcement.
- Threat Protection: Modern API gateways provide robust protection against common attacks, including rate limiting, to prevent denial-of-service attempts, input validation to filter malformed requests, bot detection to identify automated attacks, and anomaly detection to spot unusual behavior patterns.
- Centralized Visibility: Gateways simplify management by centralizing monitoring, logging, and analytics. This makes identifying potential security incidents and responding quickly much easier.
Edge Computing Security
Edge computing brings processing closer to data sources, reducing latency while introducing new security considerations:
- Micro-segmentation at the Edge: Implement micro-segmentation to isolate network segments and prevent lateral movement if one segment is compromised. This approach proves particularly effective in IoT environments where device security varies widely.
- Local Threat Detection: Edge nodes can detect and respond to threats locally before they reach your core infrastructure, creating an additional security layer that protects your primary systems.
Breaking Through Barriers: Conquering Zero Trust Challenges
Zero Trust implementation offers significant security benefits but comes with substantial hurdles. Learning from real-world case studies, we can identify practical solutions that make the difference between success and stalled initiatives. The Colonial Pipeline incident taught us that even well-protected systems can fail catastrophically with a single compromised credential.
Legacy System Integration
One significant obstacle is the incompatibility between legacy systems and zero-trust principles. Traditional systems operate on implicit trust models that fundamentally conflict with continuous evaluation requirements.
Rather than attempting a full overhaul, implement Zero Trust principles in phases:
- Start with micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement
- Deploy advanced authentication solutions for critical systems first
- Integrate endpoint detection and response tools gradually
- Replace implicit trust systems systematically over time
By approaching transformation incrementally, you can manage costs while steadily improving your security posture.
Organizational Resistance
Successful Zero Trust adoption requires active engagement from diverse stakeholders, including executive leadership, IT personnel, system owners, and end users.
- Form a dedicated team with expertise in network security, cloud architecture, endpoint security, and identity access management. This cross-functional team navigates technical challenges while serving as advocates throughout your organization.
- Secure executive support from management, as leadership sets the tone for security processes across the organization. When executives prioritize Zero Trust, resources and attention follow.
Building a Phased Rollout Strategy
Financial institutions have demonstrated success with a clear "on-ramp" strategy for Zero Trust. Rather than tackling everything at once, start with one of these focal points:
- Identity-centric approach: Begin by strengthening authentication and access controls
- Network-focused implementation: Implement micro-segmentation and traffic monitoring
- Application security emphasis: Protect critical applications with enhanced controls
- Data-centered protection: Classify and secure sensitive data first
By prioritizing one area initially, you build momentum with quick wins before expanding to a comprehensive approach. Many organizations create dedicated "Zero-Trust Task Forces" composed of specialists across different security domains to guide this phased implementation, leveraging automated workflows to streamline processes.
Security Without Friction: Keeping Developers Happy
When implementing API security, one of the greatest challenges is finding the right balance between robust protection and maintaining an excellent developer experience.
Security-Performance Trade-offs
As your API security measures become more sophisticated, you may encounter performance impacts:
- Authentication mechanisms add processing overhead
- Rate limiting requires tracking requests
- Input validation increases request processing time
Integration Strategies for Minimal Impact
To mitigate these trade-offs effectively, integrate security early in your API design phase:
- Centralize authentication and authorization through dedicated infrastructure
- Define clear data exposure requirements following least privilege principles
- Conduct threat modeling during design to implement targeted security measures
- Leverage API gateways to offload security functions
- Choose efficient security libraries known for both security and performance
- Additionally, integrating effective strategies for monetizing APIs can enhance both business value and developer engagement
By thoughtfully integrating security into your API design process, you achieve robust protection without sacrificing developer experience or performance.
The Security Crystal Ball: What's Next for Zero Trust
As Zero Trust matures, several emerging technologies and approaches are poised to further transform API security. Understanding these trends helps organizations stay ahead of both threats and opportunities.
AI-Powered Security Analytics
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how we detect and respond to API threats:
- Behavioral Analysis: Advanced AI models can establish baseline API usage patterns and automatically detect anomalies that indicate potential attacks, significantly reducing false positives compared to rule-based systems.
- Predictive Security: Machine learning algorithms can predict potential vulnerabilities before they're exploited by analyzing patterns across billions of API calls and identifying risk indicators.
- Automated Response: AI-driven systems can not only detect threats but also implement countermeasures in real-time, blocking suspicious activities before they cause damage.
Passwordless Authentication for APIs
The industry is moving beyond traditional authentication methods:
- Biometric Verification: Integration of biometric factors into API authentication flows reduces dependency on credentials that can be stolen.
- Device-Based Authentication: Using device fingerprinting and cryptographic attestation provides stronger identity verification without password vulnerabilities.
- Ephemeral Credentials: Short-lived, automatically rotating credentials significantly reduce the risk of compromise compared to static API keys or passwords.
Zero Trust API Mesh Architecture
The evolution of service mesh concepts is creating new possibilities for securing distributed APIs:
- Identity-Aware Proxies: Next-generation API meshes incorporate identity awareness at every connection point, enabling fine-grained access decisions.
- Unified Policy Management: Centralized policy engines that can enforce consistent security rules across hybrid and multi-cloud environments are becoming essential.
- End-to-End Encryption: Automatic TLS between all services, not just at ingress points, ensures data remains protected throughout its journey.
As these technologies mature, implementing Zero Trust for APIs will become both more powerful and more accessible, allowing organizations to build security into their systems from the ground up rather than adding it as an afterthought.
From Vulnerable to Vigilant: Take Action Today
Moving to a zero-trust model for your APIs delivers concrete benefits: better user experiences, improved security posture, and reduced breach risk. These enhancements minimize your attack surface, streamline security workflows, and maximize your infrastructure investments.
Ready to transform your API security with Zero Trust principles? With Zuplo's developer-focused interface and easy-to-deploy policies for API security, you can quickly bridge the gap between traditional models and modern Zero Trust protection. Sign up for a free Zuplo account today and start implementing "never trust, always verify" across your entire API ecosystem.