Enterprise Feature
Secure tunneling is available as an add-on as part of an enterprise plan. If you would like to purchase this feature, please contact us at sales@zuplo.com or reach out to your account manager.
Most enterprise features can be used in a trial mode for a limited time. Feel free to use enterprise features for development and testing purposes.
Setting up Tunnels
A tunnel is a way to expose your internal services to the Zuplo gateway
without exposing it to the public internet. Your Zuplo Gateway accesses those
services through the service:// protocol.
The easiest way to deploy your tunnel is using a Docker container. The three basic requirements for deploying a secure tunnel with Docker are:
- A tunnel secret that's provided to the Docker container as an environment
variable named
TUNNEL_TOKEN(the secret is provided by the Zuplo CLI when you create the tunnel. See creating a tunnel) - The ability for the tunnel service to make an outbound connection to the public internet to establish the secure tunnel.
- The ability for the tunnel service to make a request to your internal API by
a DNS address. (for example
https://my-service.local/api).
The tunnel can run anywhere you can deploy a Docker container. Where you deploy depends on your specific setup. To run the Docker container on your own infrastructure, refer to instructions from your cloud provider or contact Zuplo support for assistance.
Below are a few option for deploying the tunnel.
- Deploying Docker containers on Azure
- Deploying Docker containers on AWS ECS
- Deploying container images to GCP
The docker container is zuplo/tunnel and is available on
Docker Hub.
Your running container needs a single environment variable named TUNNEL_TOKEN.
You should store the value as a secret using the recommended means of secret
storage and environment variable injection for your platform.
Configuring services
Once you have created a tunnel, you can
configure which services it should expose
using a configuration file. Below is a sample configuration file. The properties
in the services objects are explained below.
name- This is the name of the service that you will use from your Zuplo projectendpoint- This is the local endpoint of your service that you tunnel can connect toconfigurations- This object specifies which projects and which environments can access this service.project- The name of the Zuplo projectaccessibleBy- The environments which can use the tunnel. Valid values areproduction,preview, andworking-copy.
tunnel-config.json
Code
Using Services Exposed through Tunnels in Code
Once set up, the services in the tunnels can be treated like any API host that
you call from your Zuplo gateway. Each service exposed through tunnels is called
with the URL schema service://, so if your service is named
my-awesome-service you will call it using the URL
service://my-awesome-service.
This URL can be used in code as shown below.
Code
It's common to have multiple services for each of your internal environments. Each service can be restricted so that it's only accessible by specific Zuplo environments. For example, you might have two services one for production and one for staging.
service://my-awesome-service-prod(Production)service://my-awesome-service-staging(Staging)
Using Services Exposed through Tunnels in Configuration
Services can also be used in routes.oas.json file such as with the URL Rewrite handler. To call a tunnel service simply use it as part of the rewrite URL as shown in the image below.
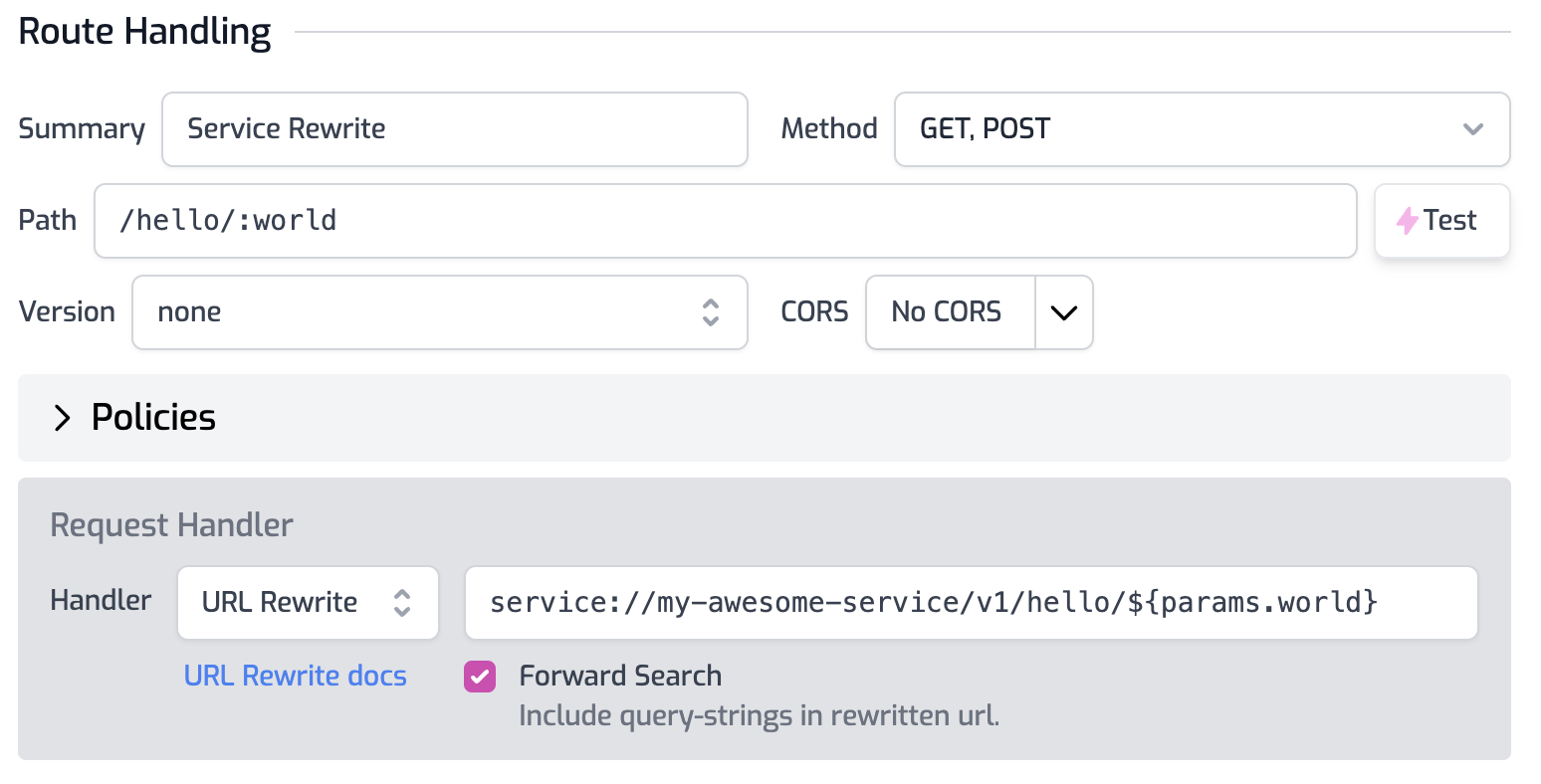
Service Environment Variables
When using these services in your code or configuration, it's often useful to store the values as an environment variable. This way you can change which environment calls which tunnel without changing code or configuration.
For the production environment you would set the BASE_SERVICE_URL to the
production service name. See
this document for more about
Environment Variables
Code
And for staging, you would use the staging service name.
Code
In your handler code or other configuration, the service can be accessed using the environment variable.
Code
Environment variables can also be used in configuration, such as the URL Rewrite handler as shown below.

Tunnel Upgrades
Zuplo publishes a new release of the tunnel Docker image about once per month or
whenever Cloudflare ships a release to their underlying tunnel tools. The most
recent version of the Docker Image is always tagged with the latest tag. We
recommend periodically checking and upgrading the tunnel to the latest release
to ensure you have the latest security and performance updates.
We recommend testing each release of the tunnel in a staging environment before rolling out to production.
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting see this document.