Caching is one of the best ways to speed up your APIs and keep users engaged. By storing frequently requested data, you avoid hitting the database for every little request — like having a cheat sheet at your desk instead of running to the library every time you need to look something up. Your response times improve dramatically, and your servers aren't strained by repetitive queries. This helps you manage sudden spikes in traffic without compromising stability.
Ready to increase your API performance and supercharge your API performance? Let's dive into the world of caching. We'll explore strategies that can turn sluggish endpoints into speed demons while keeping your infrastructure costs in check.
Understanding API Caching
Caching in APIs means temporarily storing copies of data somewhere more accessible than the primary source. When users or services request this data, they get a fast response without pulling it repeatedly from the origin.
Picture a barista who keeps a pot of coffee ready instead of brewing a fresh cup for each customer. This cuts down on database lookups and other resource-intensive operations, much like the barista saves time not grinding beans and pulling shots for every order.
In practical terms, APIs handle countless identical requests daily. Without caching, each request follows the same resource-intensive path:
- API receives request
- Backend processes the request
- Database query executes
- Results return to the client
With caching, many requests skip most of these steps, leading to lightning-fast responses and happier users. For instance, developers working with high-demand services can benefit from strategies like caching OpenAI API responses to reduce latency and improve performance.

Benefits of API Caching
Lightning-Fast Responses Users Can't Ignore
Caching transforms tedious wait times into near-instant responses. This turbocharging effect matters most for frequently accessed data that rarely changes.
When users click and see immediate results, they engage more deeply with your application. Those precious fractions of a second create an experience that keeps users from abandoning your platform out of impatience.
Server Relief When You Need It Most
By handling repeated requests without touching your database, caching significantly reduces the load on your backend systems. Your infrastructure can focus on processing unique requests that actually need computing power.
This means your architecture scales more effectively and efficiently. You can serve more users without proportionally increasing your server resources, creating a more cost-effective system that handles growing demand without breaking a sweat.
Implementing backend optimization strategies such as Backend for Frontend (BFF) patterns can further enhance performance and scalability.
Responsive Experiences That Build Loyalty
The stark difference between lagging load times and crisp responses determines whether someone stays engaged or bounces away. Users might not notice perfect performance, but they feel every slowdown.
Effective caching creates responsive experiences that build trust and keep users returning. In today's competitive landscape, this performance edge separates thriving APIs from forgotten ones.
Cost Savings That Impact Your Bottom Line
Fewer resource-intensive operations translate directly to lower infrastructure costs. Cloud providers typically charge based on computation time, database operations, and data transfer—all dramatically reduced with smart caching implementation.
When traffic unexpectedly surges, caching acts as a protective buffer for your system. Instead of frantically scaling up or watching your servers crash under load, cached responses help maintain stability even during peak times.
Strategic API Caching Locations: Where to Store Your Data
Caching can happen at multiple points in your data flow. Each approach offers unique advantages that help you balance performance and practicality. Essentially, you’re deploying several layers of defense, each catching and serving different types of requests before they hit your core systems.

Server-Side Caching: Your First Line of Defense
Server-side caching stores frequently accessed data on your API servers, dramatically reducing database queries and processing overhead. This is like having prep cooks who keep commonly ordered ingredients ready instead of preparing everything from scratch for each order.
Implementing server-side caching can be streamlined by leveraging hosted API gateway advantages, which offer built-in caching mechanisms and infrastructure benefits.
Two primary approaches dominate server-side caching:
In-Memory Caching: Lightning-Fast Access
In-memory caching keeps data in RAM for the absolute fastest retrieval speeds. Two popular solutions stand out:
Redis stands as the Swiss Army knife of in-memory caching. This open-source powerhouse supports complex data types like lists, sets, and hashes, making it ideal for sophisticated caching needs. It handles high volumes with microsecond latency and includes features for persistence and replication.
Redis excels when you need advanced data structures or want to store complex objects like user sessions, leaderboards, or real-time analytics. The trade-off? Higher memory consumption than simpler alternatives.
Memcached takes the opposite approach, focusing on simplicity and raw speed. It uses a straightforward key-value model that's ideal for quick retrieval of simple data. While it lacks built-in persistence and advanced data structures, its simplicity makes it perfect for caching basic API responses.
Disk-Based Caching: Balancing Speed and Volume
Disk-based caching isn't as lightning-fast as in-memory solutions, but it can handle substantially larger datasets and offers better durability. This approach often complements in-memory caching in a tiered strategy. Frequently accessed items stay in memory for instant retrieval, while less common but still important data lives on disk—still faster than regenerating it from scratch.
The right choice depends on factors like load expectations, data volume, and resource availability. Many APIs implement both approaches, using in-memory caching for hot data and disk-based solutions for everything else.
Client-Side Caching: Empowering the Front End
Client-side caching stores data directly on your users' devices, eliminating server requests entirely for repeat data. It's like giving customers their own mini-warehouse so they don't need to visit your distribution center for every item.
Several implementation methods offer different strengths:
localStorage persists data indefinitely (or until manually cleared), making it perfect for items that rarely change.
sessionStorage works similarly but clears when the browser session ends, ideal for temporary state.
Cookies handle small data needed on every request, though they increase header size.
Service Workers enable advanced caching patterns including offline functionality.
This approach dramatically improves user experience when multiple API calls target the same endpoint. For example, an e-commerce application can cache product details, making browsing similar items feel instantaneous rather than waiting for repeated server responses.
Understanding different methods and tools for caching APIs effectively is crucial for optimizing client-side performance.
Edge Caching and CDNs: Global Speed Optimization
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) distribute cached data across global edge servers, positioning your content physically closer to users regardless of their location. Imagine having identical convenience stores in every neighborhood instead of one central market—people get what they need faster because the physical distance is minimized.
By operating API on edge, you can significantly reduce latency and improve user experience worldwide.
This approach delivers several key advantages:
- Reduced latency: Data travels shorter physical distances to reach users
- Improved reliability: If one edge server fails, others seamlessly take over
- Better load distribution: Traffic spreads across many servers rather than concentrating on your origin
- DDoS protection: Edge networks can absorb attack traffic before it reaches your infrastructure

Implementing API Caching: A Practical Approach
A solid caching strategy includes server-side techniques, smart client-side caching, and effective use of CDNs. Let's break down the practical implementation steps for each approach:
Server-Side Caching Implementation
Identify Cacheable Data: Not all API responses should be cached. Decide which responses can tolerate minor delays before updates. Good candidates include:
- Reference data that changes infrequently (product categories, geographic information)
- Aggregated statistics that don't need real-time accuracy
- Search results that don't change by the second
Use Cache-Control Headers: HTTP headers are your primary tool for controlling caching behavior. Configure headers like Cache-Control, Expires, and ETag to govern caching behavior:
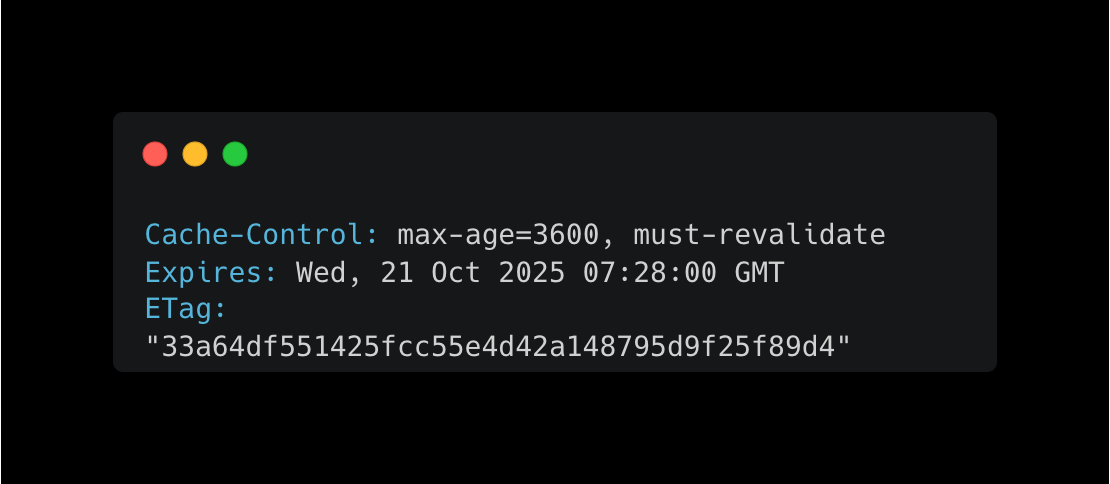
These headers tell clients and intermediate caches how long to store the response and when to check for updates.
For more information on configuring caching policies, refer to detailed documentation.
Implement with Middleware or Libraries: Most web frameworks offer caching middleware that simplifies implementation. Tools like Redis are popular for handling cached data in Node.js or similar stacks. Alternatively, using ZoneCache for APIs provides a managed solution for server-side caching.
For example, in an Express.js application:
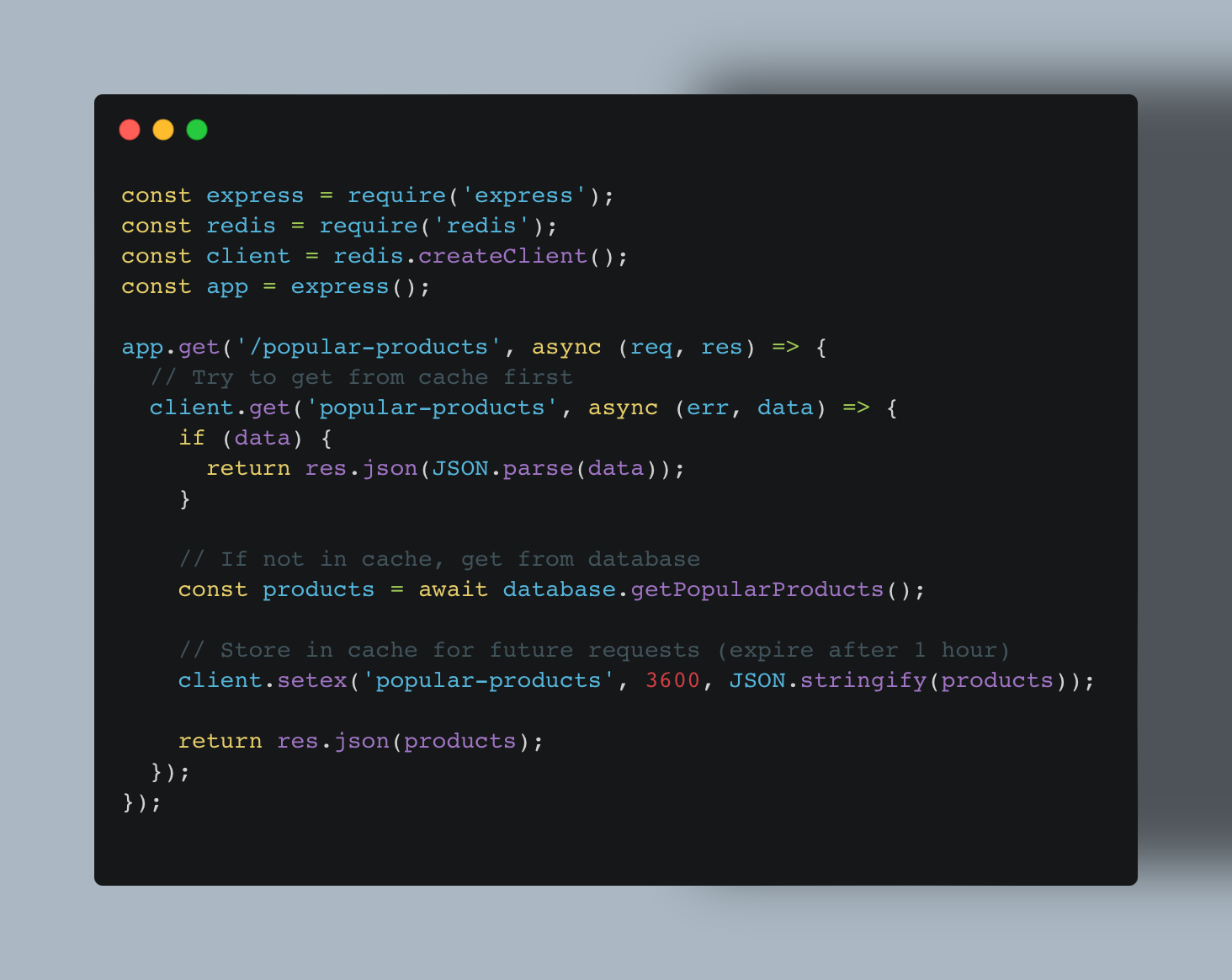
Plan for Invalidation: When cached data changes, you need a reliable approach to refresh it. Options include:
- Set appropriate TTL (Time-To-Live) values based on how frequently data changes
- Implement cache-busting mechanisms that update cache when the underlying data changes
- Use event-based systems where data updates trigger cache invalidation
Additionally, utilizing custom domains for APIs can aid in managing cache invalidation policies across different services.
Optimizing Client-Side Caching
Browser Caching: Let browsers hold onto frequently used files like images, JavaScript, or stylesheets. Configure your API to send appropriate cache headers for static resources:
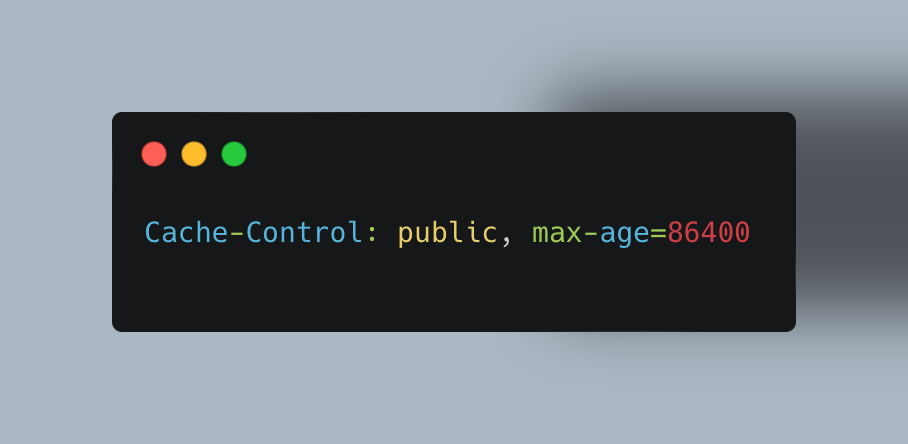
This tells browsers they can cache the response for up to 24 hours.
Service Workers: For more advanced applications, service workers can store certain API responses for rapid retrieval, even offline:
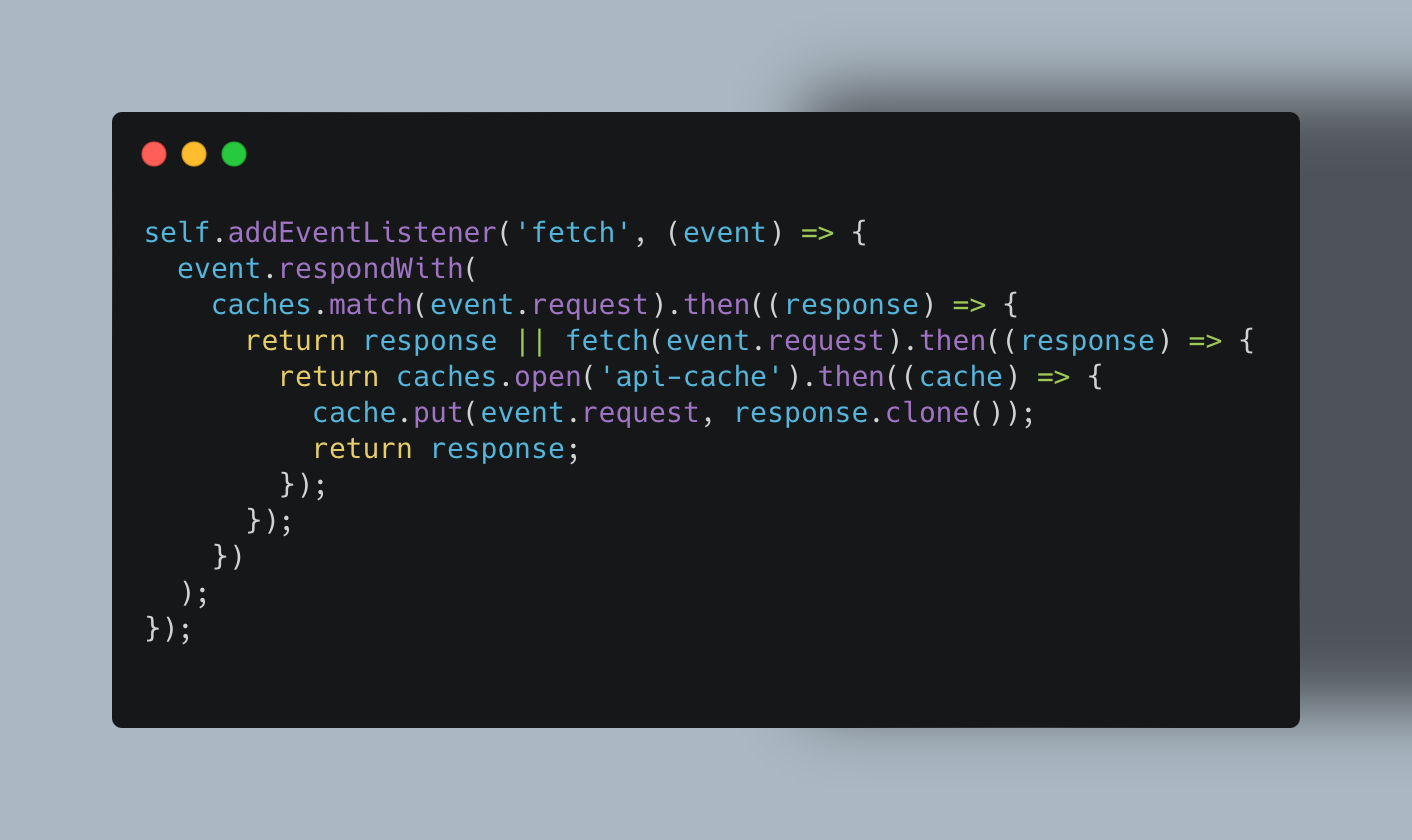
Cache API: Modern browsers offer a Cache API that lets you save request-response pairs for repeated use without always hitting the network:
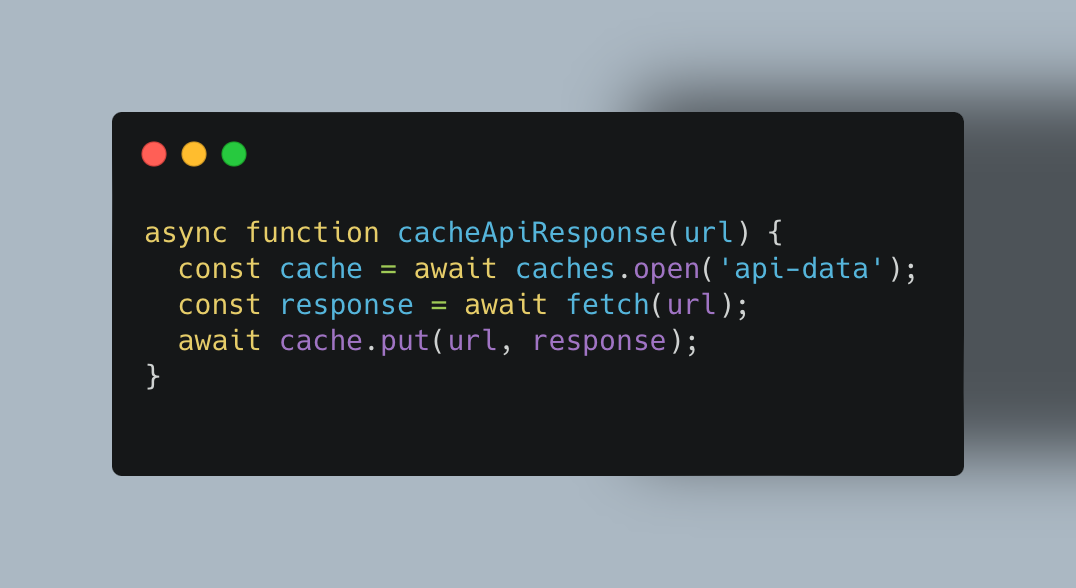
Leveraging CDNs Effectively
CDNs position your cached content closer to users worldwide, dramatically reducing latency and server load.
Strategic Content Lifetimes
Assign appropriate TTLs based on content volatility. Static resources (images, CSS) can cache for weeks, API responses for hours, and frequently updated content for minutes. Keep user-specific data minimally cached unless properly secured.
Edge Rule Configuration
Use your CDN's dashboard to create custom caching rules by content type or URL pattern. Configure different behaviors for stable endpoints (product listings) versus dynamic ones (inventory status).
Performance Monitoring
Track cache hit ratio, origin traffic reduction, geographic response times, and bandwidth usage. Aim for hit ratios above 90% and optimize edge server placement based on user location data.
Strategies for Cache Invalidation
Cache invalidation keeps data fresh when updates occur. Without it, users might see stale results that can lead to confusion or errors. It's one of the two hard problems in computer science (along with naming things and off-by-one errors).
Additionally, implementing API rate limiting best practices ensures your API remains efficient and reliable under varying load conditions.
Understanding Cache Invalidation
Manual Invalidation: The application explicitly marks or removes outdated data. This offers tight control but requires careful upkeep. For example, when a product price changes, your code explicitly invalidates that product's cache entry:
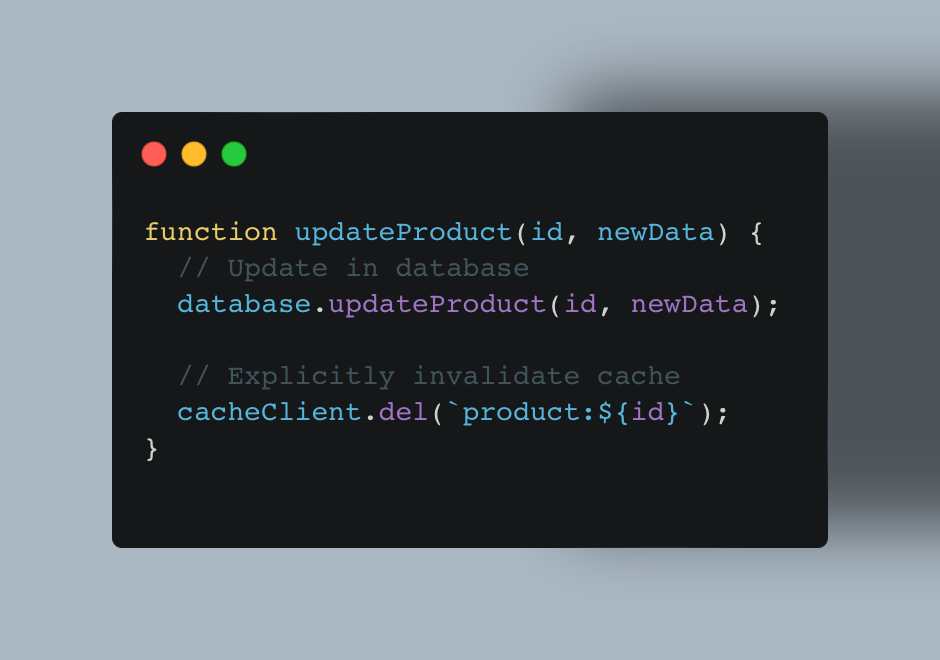
Time-to-Live (TTL): Cache entries expire automatically after a set period. It's easier to set up but can trigger unneeded cache rebuilds:
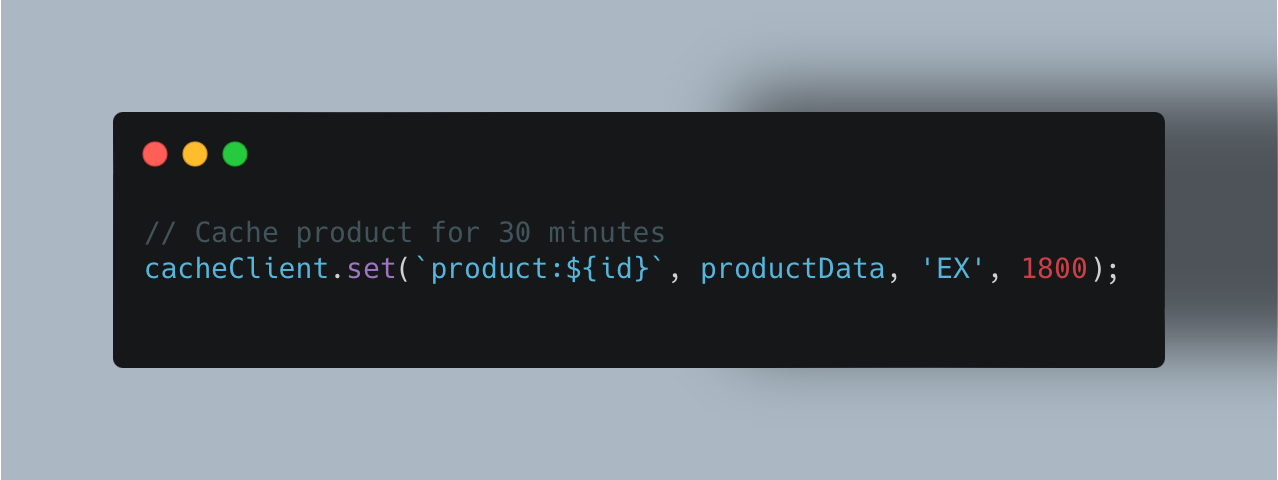
The simplicity makes this approach popular, but it means some cached data might expire before it changes, causing unnecessary recomputation.
Automatic (Passive) Invalidation: The cache monitors the primary data source for changes. It's efficient for real-time updates but needs a robust setup. This often involves event-driven architectures:
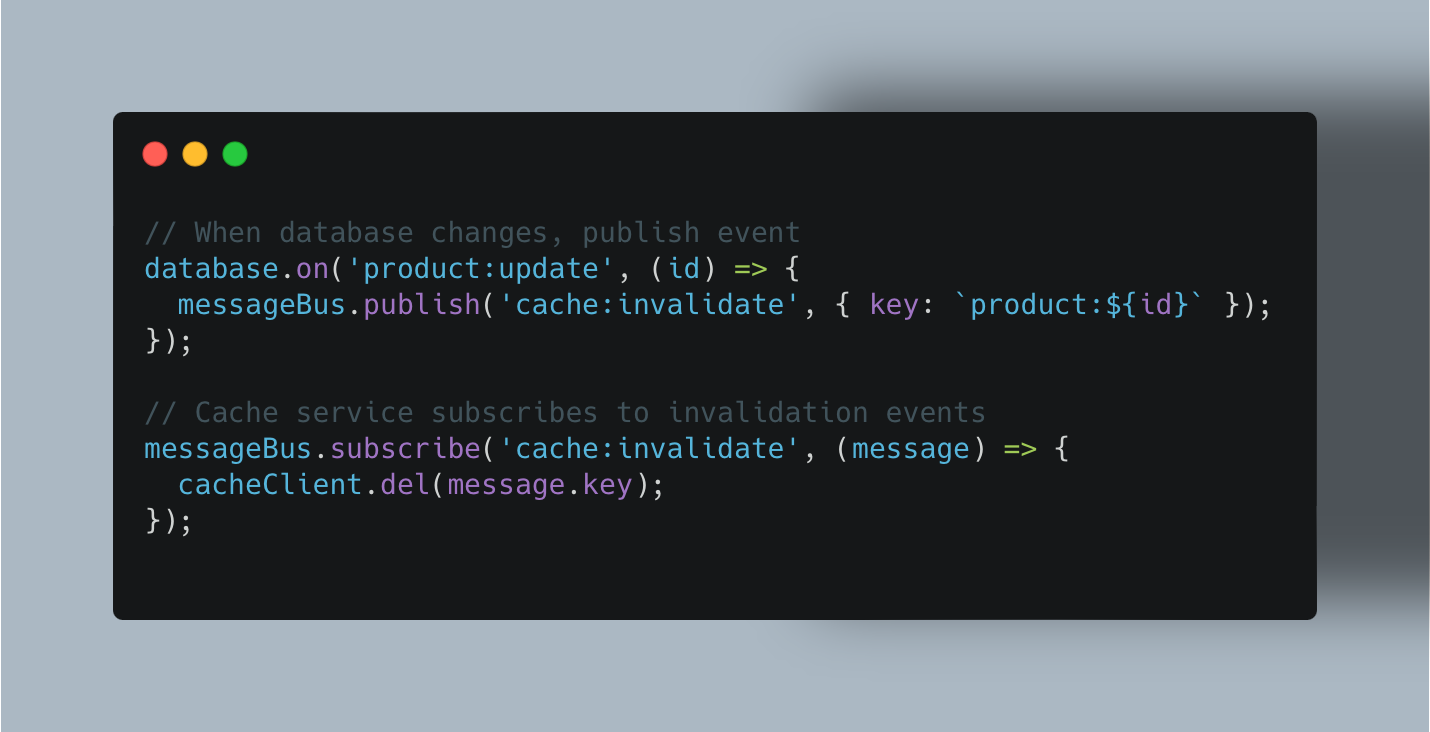
Trade-offs and Challenges
Balancing freshness, performance, and complexity is tricky. Manual invalidation is precise but introduces overhead. TTL avoids outdated data but might cause bursts of cache misses when many items expire at once. Automatic invalidation is convenient if your system can reliably detect and publish changes to the cache.
To combat this, many successful APIs combine approaches—using TTL as a fallback while implementing event-based invalidation for critical data changes.
Common API Caching Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced developers encounter challenges when implementing caching. Here are the most common issues and their solutions:
Over-Caching vs. Under-Caching
Problem: Caching too aggressively leads to stale data, while insufficient caching fails to deliver performance benefits.
Solution: Analyze data volatility and access patterns. Highly dynamic data needs shorter TTLs or real-time invalidation, while stable information can cache longer. Monitor cache hit rates and adjust accordingly.
Cache Stampedes
Problem: When popular cache entries expire, multiple simultaneous requests trigger redundant database queries—potentially overwhelming your backend.
Solution: Implement cache warming for critical data and use techniques like "cache locks" to prevent duplicate regeneration:
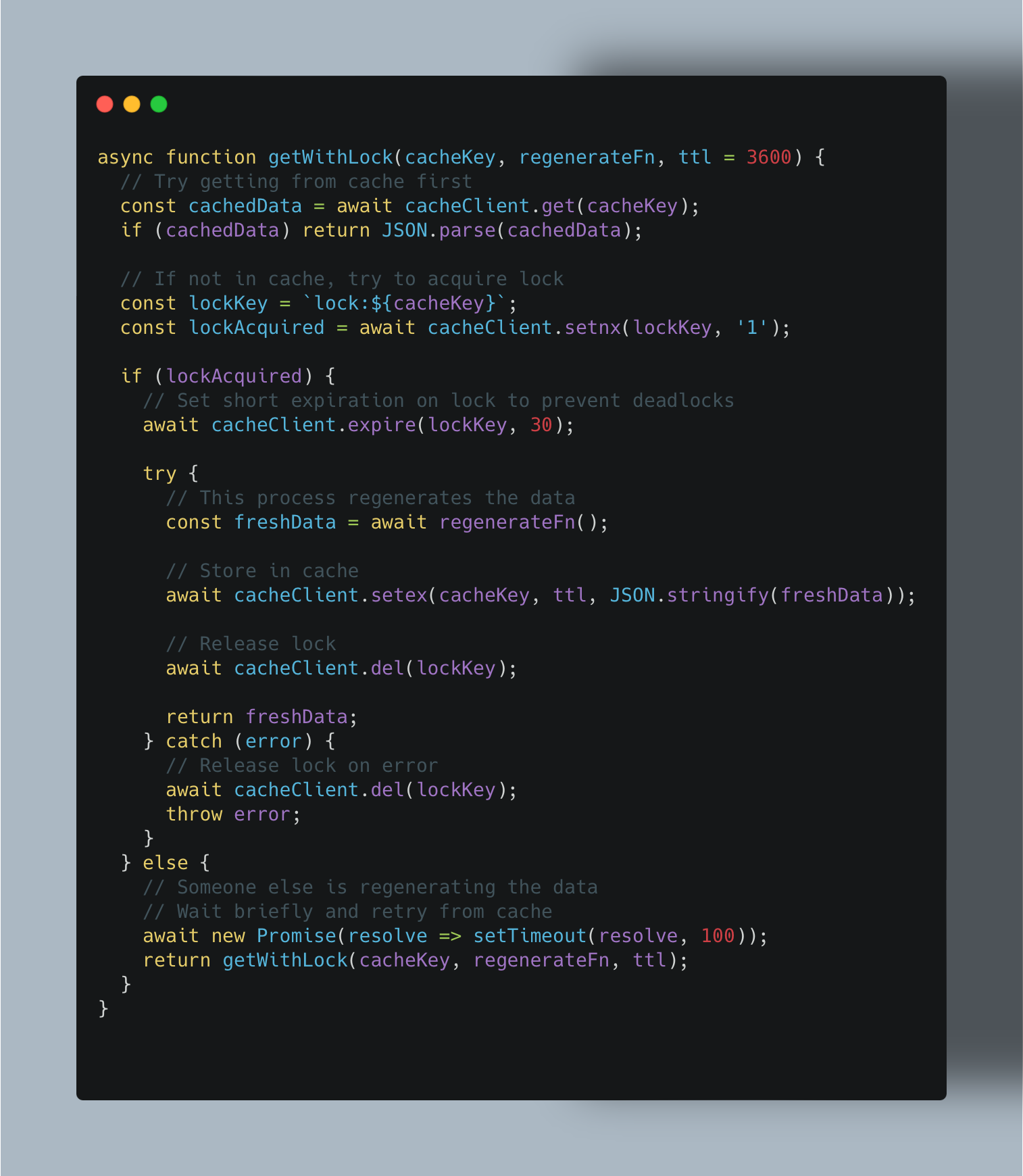
Implementing effective rate limiting strategies can mitigate this issue by controlling the flow of requests to your API.
Memory Management Issues
Problem: Unchecked cache growth consumes excessive resources, while insufficient memory causes frequent evictions.
Solution: Set appropriate maxmemory configurations in Redis or similar systems, and choose efficient eviction policies:
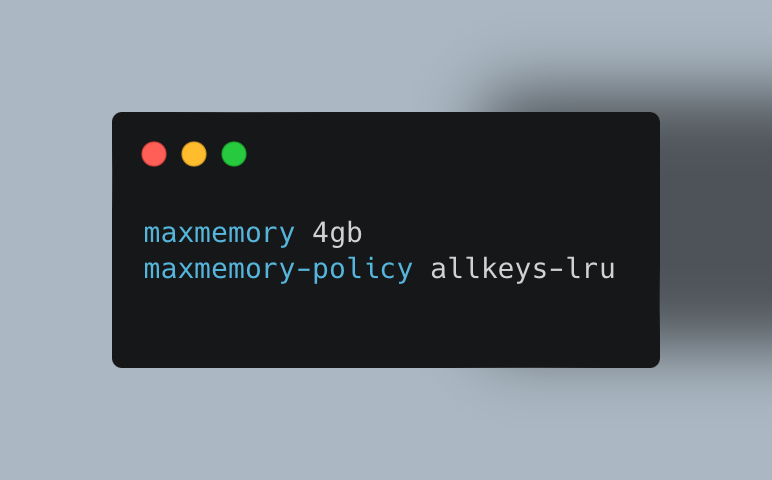
This configuration limits cache size to 4GB and removes least recently used items when memory fills up.
Security Concerns
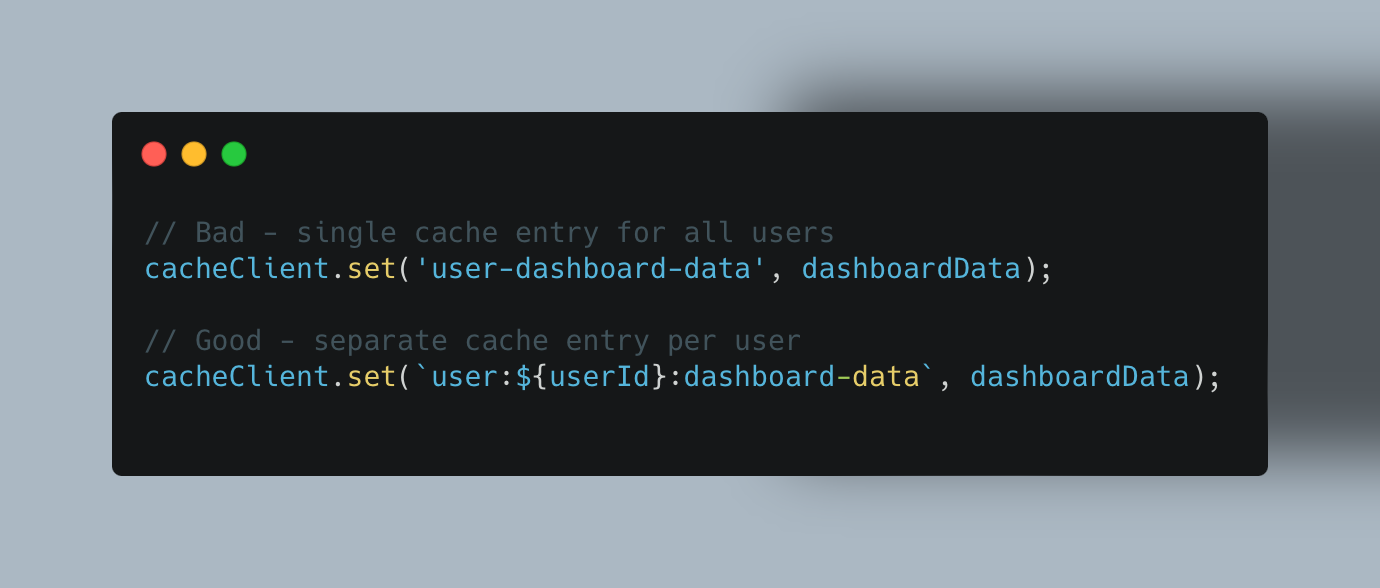
Problem: Cached data might contain sensitive information accessible to unauthorized users.
Solution: Never cache personally identifiable information (PII) or authentication credentials. For user-specific data, include user identifiers in cache keys:
Advanced Caching Techniques for High-Traffic APIs
High-traffic APIs demand sophisticated caching and precise monitoring to ensure smooth performance. As your API scales, these advanced techniques become increasingly valuable.
Advanced Strategies
Edge Caching: Distribute responses across CDN edge nodes to reduce latency for global applications.
Stale-While-Revalidate: Let users receive slightly outdated data while the cache updates in the background:
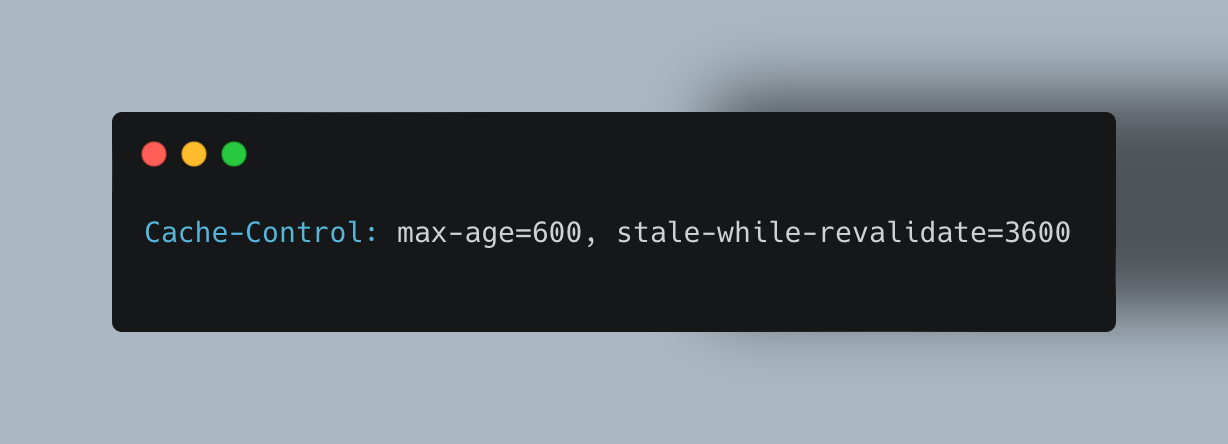
This allows cached data use for 10 minutes without checking, and up to an hour with background revalidation.
Smart Invalidation: Tag or hash cached entries so only relevant items get invalidated when content changes, avoiding unnecessary purges.
Cache Warming: Proactively populate cache before peak times to prevent the "thundering herd" problem:
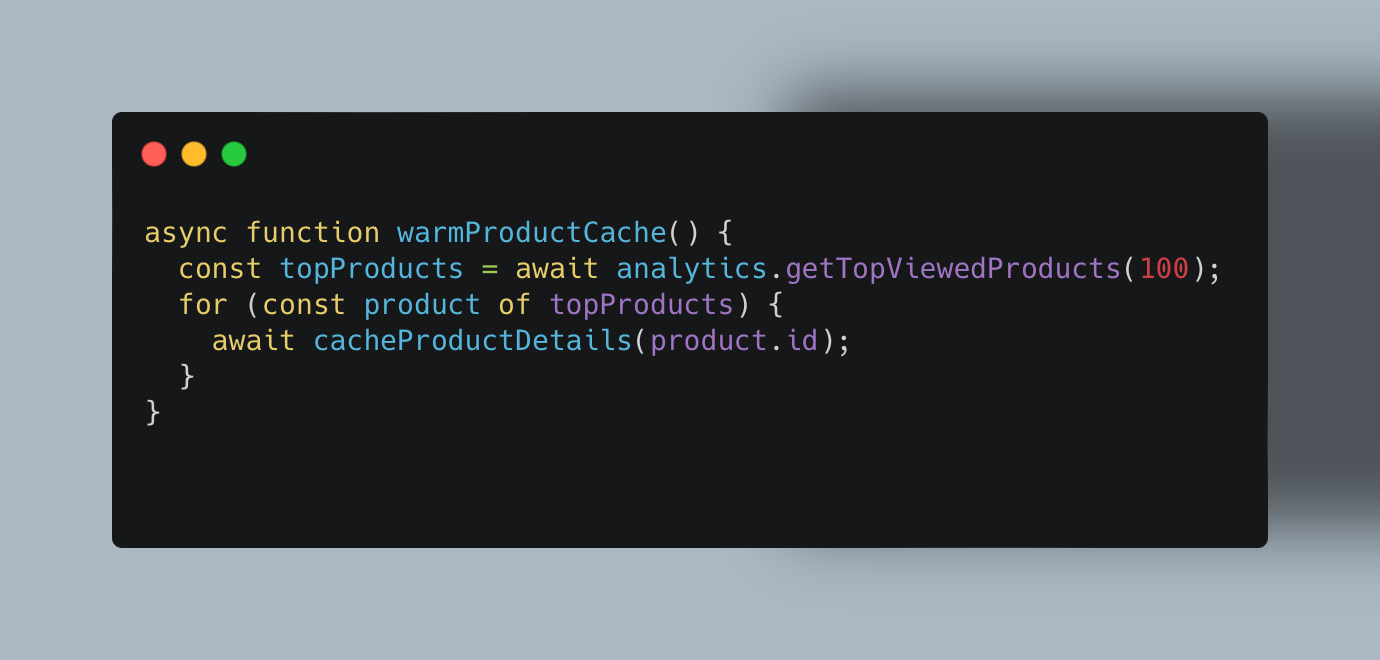
Additionally, implementing lazy load configuration can enhance cache efficiency by loading data only when needed.
Partial Cache Updates: Update only changed portions of cached data, particularly useful with GraphQL APIs.
Performance Tuning and Monitoring
Track Hit Rates: Keep tabs on how often the cache serves a request to optimize your cache rules. Low hit rates suggest your caching strategy needs adjustment.
Load Testing: Determine if your caching setup can handle peak usage without slowing down. Simulate traffic spikes to identify potential bottlenecks before they affect real users.
Real-time Alerts: Spot anomalies quickly by monitoring response times, error rates, and cache storage patterns. Set up alerts for:
- Sudden drops in cache hit rates
- Increased origin server load
- Spikes in response time
- Cache memory approaching limits
Monitoring for errors, such as the HTTP 431 status code, is also important. Our HTTP 431 error guide provides insights into diagnosing and resolving such issues.
Geographic Analysis: Review performance across regions to ensure all users get fast responses. Optimize edge caching for areas showing higher latency.
Wrapping Up: Caching as a Competitive Advantage
Implementing effective caching isn't just a technical optimization—it's a business advantage that directly impacts user satisfaction and operating costs. By reducing latency and offloading backend systems, you deliver lightning-fast responses while keeping your infrastructure lean. The right caching strategy balances freshness with performance, giving users the responsive experience they demand without sacrificing accuracy.
Ready to supercharge your API performance? Zuplo's platform makes implementing advanced caching strategies simple with declarative policies that integrate seamlessly with your existing workflow. Sign up for a free Zuplo account or book a demo with us and transform your API speed in minutes.